In project management, you may be familiar with the adaptive and predictive approaches or even worked with both of them at different points. But do you know the differences between them?
Projects are unique and no two projects are entirely the same. They may have the same scope and requirements, but there are lots of factors that are invariably unique to each ranging from risks, stakeholders, and constraints.
Thus, the methodology, lifecycle, and processes used for each project should be tailored according to its nuances.
While the traditional predictive or waterfall methodology has been used for ages for lots of projects, modern rapidly changing business needs require a more adaptive approach.
In this post, we compare the adaptive vs predictive project management approaches over their differences, and life cycle. Also, we cover when best to use an adaptive or predictive approach, and when to combine both.
What is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a structured approach that serves as a blueprint for managing projects, by outlining procedures, tasks, resources, and stages involved in project execution.
Project management methodologies such as Agile, Scrum, or waterfall offer unique approaches to project planning, task division, and progress tracking, tailored to different project types and industries.
They help manage risks, maintain quality, and ensure projects are completed on schedule and within budget using their unique methods.

Adaptive vs Predictive Project Management Overview
Common project management approaches include predictive and adaptive methodologies. They each have their strengths and weaknesses depending on project goals, team dynamics, and work environment.
A project should be assessed by its needs, resources, timelines, and risk tolerance to select an approach that guides its life cycle, planning, execution, monitoring, and completion.
Adaptive Approach in Project Management
Adaptive project management is an iterative approach to managing projects that embraces change as a normal part of the process.
The adaptive approach involves continuously re-planning and adjusting the project timeline, resources, and scope as new information emerges.
It assesses risk frequently, gets feedback from stakeholders often, delivers work in small increments, and makes necessary adjustments to reduce uncertainty and adapt the project plan to match the evolving circumstances.
The adaptive approach in project management emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and learning to maximize the likelihood of project success in complex, uncertain environments.
Predictive Project Management Approach
Predictive project management, also known as waterfall project management, is a structured, linear approach that emphasizes detailed upfront planning and strict adherence to that initial plan.
It assumes the project scope, timeline, and costs can be accurately predicted at the outset, and generally follows a sequence of define, design, build, and test.
Requirements are gathered early, resources are allocated, tasks are scheduled, and the project team implements each predetermined phase. There is limited flexibility to change course once execution starts.
Adaptive vs Predictive Project Management Life Cycle
The project life cycle is the series of phases that guide the project from start to completion. It provides a structure for managing and completing projects based on the project management approach employed.
Adaptive Life Cycle in Project Management
The adaptive life cycle, synonymous with Agile methodologies, is a flexible approach to project management that functions through iterative cycles or Sprints, with each providing an opportunity for adjustment based on stakeholder feedback and changing project requirements.
This approach prioritizes customer satisfaction, promoting a collaborative team environment, and the capacity to rapidly respond to change.
Unlike traditional methodologies, the adaptive life cycle places a higher value on producing functioning results over rigid adherence to predetermined plans, making it ideal for projects with volatile or unclear requirements.
Predictive (Waterfall) Life Cycle in Project Management
The predictive life cycle, commonly referred to as the waterfall model, is a linear and sequential approach in project management. It starts with comprehensive planning, where every stage of the project is defined upfront.
Once the planning phase is complete, changes are typically challenging to implement and each phase must be fully completed before the next begins, following a cascading effect like a waterfall.
This waterfall model is particularly suited for projects with well-defined, static requirements, and a well-understood technology base, where the scope, time, and cost factors are clearly outlined from the beginning.
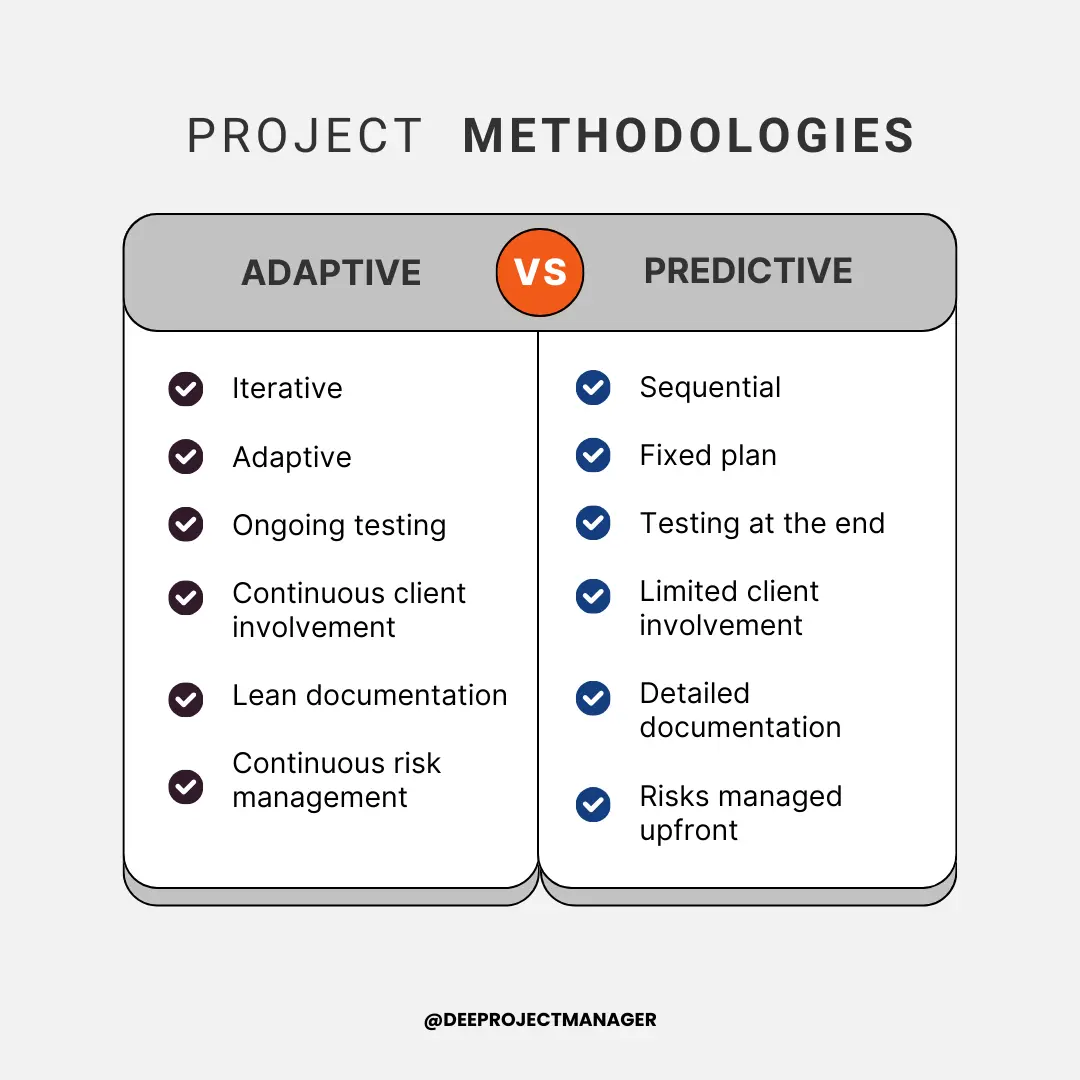
Adaptive vs Predictive: Key Differences
Having gotten an overview of the adaptive and predictive approaches to project management, let’s go into the key differences between them.
1. Planning and Structure
In predictive project management, the entire project is planned in detail at the beginning. This includes setting timelines, determining resources, and outlining the project’s scope.
It’s a linear and sequential approach where the next phase begins only after the completion of the current phase.
In contrast, adaptive project management is more flexible and iterative. Projects are broken down into smaller chunks or iterations.
After each iteration, the team reviews the progress and makes necessary adjustments for the next cycle. The planning is done progressively throughout the project lifecycle.
2. Change Management
Change is managed very strictly in predictive project management. Any alterations to the scope, time, or cost are usually avoided, and if unavoidable, they go through a formal integrated change control process.
Adaptive project management on the other hand embraces change and treats it as a key part of the project that provides valuable feedback and opportunities for improvement. Changes are easily accommodated in the next iteration.
3. Stakeholder Involvement
In predictive project management, stakeholder involvement is generally limited to the beginning and the end of the project. Feedback is typically collected during the requirements gathering phase and at the project delivery stage.
Adaptive project management involves stakeholders throughout the project life cycle.
Regular feedback is sought after each iteration, and adjustments are made based on this feedback to ensure that the final product is closely aligned with stakeholder expectations.
4. Project Scope
In predictive project management, the scope of the project is clearly defined and fixed at the start of the project and any changes to the scope require rigorous change control procedures.
In adaptive project management, the scope isn’t fixed and can evolve over time. This flexibility allows the team to prioritize and adjust the project’s features based on ongoing feedback and changes in the business environment.
5. Risk Management
In predictive project management, potential risks are identified, analyzed, and planned for at the beginning of the project. It’s more proactive in managing risks, but it may not adapt well to new risks that emerge during project execution.
Adaptive project management takes an iterative approach to risk management. Risks are continually reassessed and managed throughout the project cycle. This ongoing risk assessment allows the team to respond quickly and effectively to new risks.
6. Documentation
Predictive project management emphasizes documentation. Detailed project plans, requirements specifications, design documents, and other artifacts are created to ensure everyone has the same understanding of the project.
Adaptive project management values working software over comprehensive documentation. While documentation isn’t ignored, it’s kept as lean as necessary, with the focus on delivering a working product.

When to Use Adaptive Approach for Project Management
An adaptive approach to a development project is best used for projects with uncertain or dynamic requirements, and where rapid feedback is necessary.
It is ideal for software development, product development, or any innovative project where the end product isn’t clearly defined.
The approach allows for continuous improvement and adaptation, ensuring the outcome meets the evolving needs of stakeholders.
It’s also useful for projects in fast-paced industries where changes are frequent. Examples include developing a new app, designing a new product based on customer feedback, or implementing an innovative marketing strategy.
When to Use a Predictive Approach for Project Management
The predictive approach is well-suited for projects with well-defined, stable requirements, and where the outcome is clear.
These include construction, manufacturing, or any project where tasks are sequential and changes are minimal.
The approach ensures thorough planning, risk anticipation, and a clear path to the project’s goals, making it ideal for large-scale, complex projects with fixed deadlines and budgets.
Examples include building a bridge, setting up a manufacturing plant, or implementing a known software system across an organization.
Hybrid Project Management: Combining Predictive and Adaptive Approach
As the name suggests, hybrid project management is an approach that combines elements of both predictive or waterfall, and adaptive approaches. It provides flexibility where needed while maintaining structure and control where necessary.
A project might start with a predictive approach for the planning phase, defining clear objectives, and outlining overall project structure. Then, it may shift to an adaptive approach during execution, allowing for iterative development and regular feedback.
This approach provides the best of both worlds, combining the detailed planning benefits of predictive management with the flexibility and adaptability of adaptive management, and is useful for projects that require a firm structure but also need room to adapt to changes or uncertainties.
Examples of hybrid project management include software development projects that have a clear overall objective, yet require flexibility in design and functionality based on user feedback and testing.
If you require more insight into the role and characteristics of hybrid approaches to project management, this article is helpful.
Conclusion
Deciding the approach or methodology for managing a project is to key its success and should be done from the project initiation.
Adaptive and predictive project management represent different philosophies for managing projects in dynamic environments.
Adaptive approaches focus on agility, iteration, and embracing change, while predictive approaches emphasize upfront planning and minimizing deviations.
The optimal approach depends on the project environment and objectives. Many organizations find a hybrid model works best, blending adaptive tactics like iterative delivery with predictive structures for budgeting and scheduling.
FAQs
Is Agile Predictive or Adaptive Approach?
Agile methodology is an adaptive approach that embraces change, flexibility, and continuous improvement in dynamic environments with a focus on iterative delivery and responding to feedback over following a predictive plan.
Is Agile the Same as Adaptive?
Agile project management shares many similarities with adaptive approaches, but they are not exactly the same. Adaptive approaches generally refer to any methodology that embraces change, iteration, and flexibility.
Agile is one specific methodology within the broader category of adaptive approaches, with practices like sprints, stand-ups, and user stories.
So while Agile is adaptive, the adaptive approach encompasses a wider range of methodologies beyond just Agile.