Have you recently heard about Innovation Sprints and are mulling over the idea of using them on some of your projects? Well, you certainly are not alone.
Agile Innovation Sprints are a popular new approach for driving rapid ideation, prototype development, and problem-solving such that cross-functional teams can go from an initial concept to a tested prototype in just a few days by using this approach.
This article covers the basics of what an Innovation Sprint is, the ideal time to use it, and how to run one effectively enabling you to take your ideas and turn them into reality through a fast-paced, collaborative design process.
What is an Innovation Sprint in Agile?
An Innovation Sprint is a time-bounded, structured framework for developing ideas and solutions quickly by bringing together key stakeholders in a highly collaborative, design-thinking environment to tackle problems and ideate on opportunities.
These Sprints provide intense bursts of creativity to progress from problem to tested solution, enabling organizations to respond quickly in fast-paced markets.
Innovation Sprints typically run for 3-5 days and utilize exercises like brainstorming, prototyping, and testing to progress rapidly from an initial concept to a viable product or solution.
Cross-functional teams work intensively in Sprints, diverging and converging on ideas. Divergent thinking generates many creative ideas, while convergent thinking narrows down to the most promising solutions.
The structured Sprint process focuses the team and heightens creativity amid tight timelines leading to accelerated innovation compared to traditional elongated development cycles.
An Innovation Sprint yields tangible outcomes like a product prototype, feature spec, or business plan. The key is quickly validating and iterating on ideas through continuous customer feedback.
Some common activities in an Innovation Sprint are ideation sessions, lightning talks, design studios, building prototypes, and usability testing.

What is the Goal of an Agile Innovation Sprint?
The main goal of an Innovation Sprint is to rapidly validate and advance a new product, service, or internal process from idea to prototype.
Rather than slowly developing ideas in silos, it provides intensive focus and collaboration to test and evolve concepts quickly.
The tight timeline pressures teams to prioritize speed while an experienced facilitator guides the team through structured design thinking exercises that extract the maximum creativity in a short burst.
By the end of the Sprint, the goal is to have evidence that an idea will work and be viable. This typically involves building a realistic prototype and gathering customer feedback through testing.
Prototyping rough concepts quickly lets you fail fast and learn. Teams can discard flawed ideas before wasting too much time and resources.
The Sprint goal is tangible progress on a problem, not theoretical discussions. Cross-functional teams aligned on targets often achieve more in a few days than months of traditional development.
With clear objectives, defined roles, and an Agile process, they help teams maintain focus. The goal is to tap your organization’s creative potential and quickly build momentum on the most promising ideas.
They enable organizations to respond swiftly to opportunities through rapid experimentation. The accelerated timeframe compresses months of learning into just a few days.
When to Use Innovation Sprints
Innovation Sprints are versatile and can be applied to various challenges and opportunities. Here are some of the most common situations where they are valuable:
Developing New Products and Features
Innovation Sprints are perfect for rapidly exploring and prototyping new products or feature ideas as they compress months of learning into just days.
The accelerated timeline allows you to quickly validate concepts and make evidence-based decisions about what to build next.
Solving Complex Business Problems
Many complex business challenges require innovative solutions. An innovation Sprint can focus an interdisciplinary team to rapidly ideate and test solutions to problems like improving customer retention or breaking into new markets.
The fresh perspectives and structured exercises facilitate creative problem-solving.
Overcoming Innovator’s Block
Sometimes organizations lose momentum and struggle to generate new ideas. An Innovation Sprint reinvigorates teams and combats innovator’s block through intensive creative sessions.
The fresh approaches break entrenched mindsets to uncover innovative solutions.
Strategic Planning
Innovation Sprints enable strategic planning and alignment through collaboration, prototyping, and feedback.
Rather than theoretical discussions, hands-on exercises drive concrete outcomes and buy-in on strategic projects and initiatives.
Building an Innovation Culture
Innovation Sprints showcase the benefits of focusing creative efforts. The hands-on, outcome-driven process builds organizational enthusiasm for innovation and human-centered design.
This instills a culture of experimentation and continuous learning through repeated doing.

How to Run an Innovation Sprint
Running an effective Innovation Sprint requires careful preparation, facilitation, and follow-through. Here are key steps to execute a successful one:
Define the Sprint Focus
Start by defining a clear problem or opportunity for the Sprint to tackle. This focus should align with strategic goals and have potential for creative solutions. Avoid overly broad or vague themes that lead to unfocused work.
Assemble a Cross-Functional Team
Bring together 6-8 individuals from different functions and roles as diversity of perspectives is key. Include subject matter experts as well as people unfamiliar with the topic to spur fresh thinking and appoint a skilled facilitator.
Create a Schedule
Allocate 3-5 days for a full-time Innovation Sprint. Block team members’ calendars and secure a venue. For longer Sprints, plan key milestones and daily goals. Prepare materials like whiteboards, post-its, and prototyping supplies.
Kick-off the Sprint
Brief the team on the Sprint focus, roles, and schedule. Frame the challenge as an inspiring call to action, and establish ground rules like trusting the process and deferring judgment.
Diverge on Solutions
Facilitate brainstorming and ideation sessions to generate wide-ranging ideas. Encourage wild creativity. Build on others’ ideas. Avoid judging prematurely. Capture everything and group-related solutions. Look for themes and patterns.
Converge on Options
Narrow down concepts using criteria like feasibility, customer value, and ability to prototype. Combine complementary ideas. Distill the most promising solutions and discard inferior options. Decide what to prototype and test.
Prototype and Test
Build realistic prototypes rapidly to make ideas tangible. Simple designs allow quick refinement. Gather user feedback through techniques like interviews and usability tests. Observe how customers interact with the prototypes.
Refine and Reflect
Process user insights and refine the prototypes and concepts. Identify pivot points, discuss what worked well and what could improve, update plans based on learnings and continue iterating, and then capture key learnings and next steps.
Benefits of Innovation Sprints
Innovation sprints offer a ton of advantages especially when compared to traditional prolonged development cycles.
1. Accelerated Learning
Rapid prototyping and user testing allow teams to learn in days rather than months as quick feedback loops enable faster iteration.
2. Reduced Risk
By testing rough concepts with real users, flaws are identified early before significant investments are made which helps in avoiding the squandering of resources on ideas without traction.
3. Alignment
Cross-functional collaboration during the Sprint builds shared understanding and commitment to ideas across the organization.
4. Fresh Perspectives
The structured exercises and diverse teams counter groupthink and everyday work patterns to uncover fresh perspectives.
5. Culture of Innovation
Innovation Sprints motivate teams through tangible outcomes, and this hands-on, experiential approach reinforces a culture of experimentation and creativity.
6. Cost Efficiency
Innovation Sprints eliminate wasted time on ideas lacking traction by compressing months of development and learning into a few days which is extremely cost-efficient.
7. Adaptability
The rapid process equips organizations to nimbly respond to changing customer needs and market conditions.
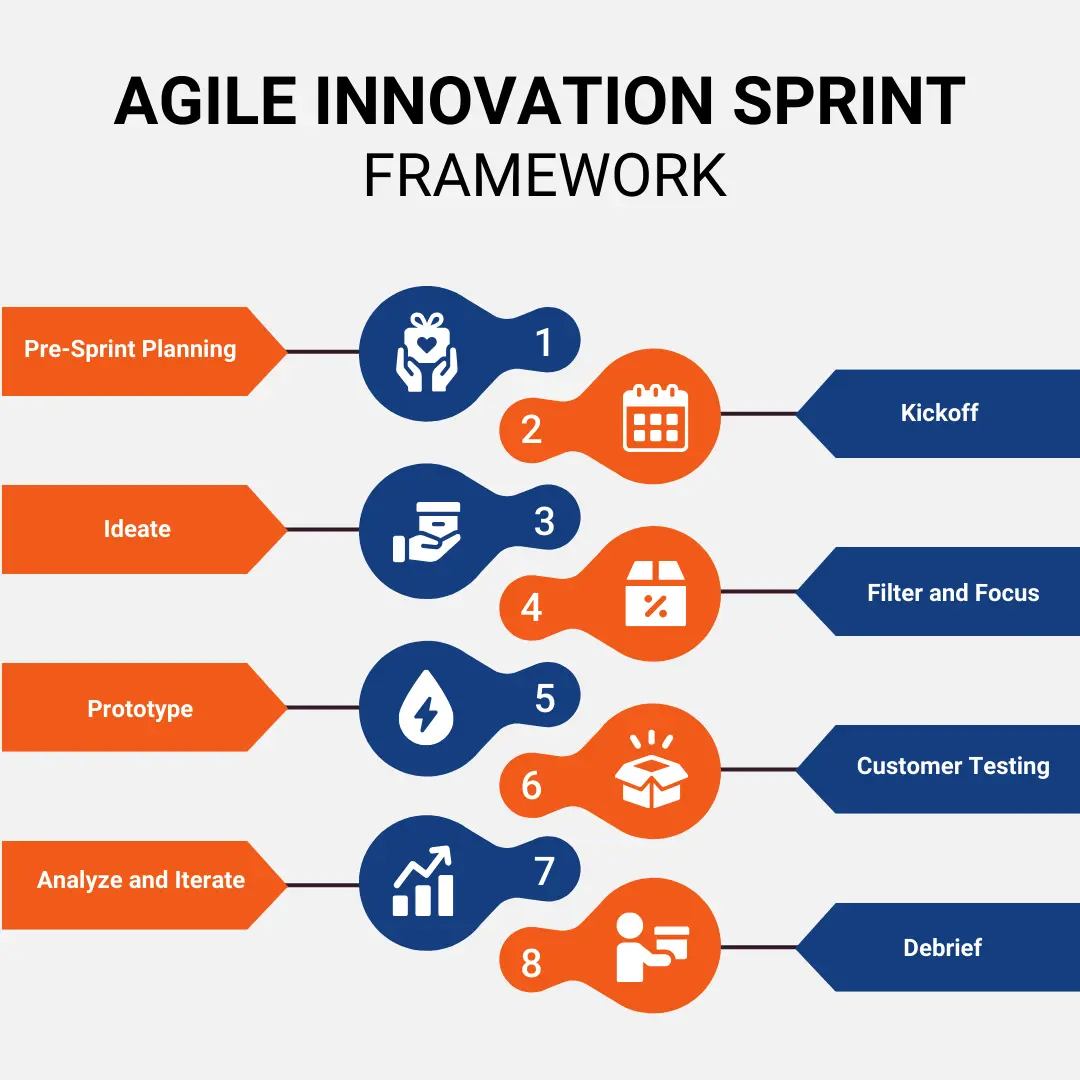
The Innovation Sprint Framework
While Innovation Sprints should be adapted to each organization’s needs, most follow a similar framework:
Pre-Sprint Planning
Determine Sprint objectives, resources, venue, and team. Select an experienced facilitator and provide background materials to align the team.
Kickoff
Brief the team on the process, objectives, and the problem(s). Frame the challenge that inspires the team, then establish ground rules and team norms.
Ideate
Facilitate brainstorming to generate wide-ranging creative solutions. Push for quantity of ideas without judging quality early, and build on each others’ ideas.
Filter and Focus
Review all ideas and filter using criteria like impact, feasibility, and uniqueness. Identify underlying themes, and pick the top solutions to prototype.
Prototype
Build rough but realistic prototypes rapidly to make ideas tangible. Simple and low-fidelity prototypes are preferred for quick testing and iteration.
Customer Testing
Gather feedback on prototypes through techniques like customer interviews, usability tests, and observation to deeply understand user perspectives.
Analyze and Iterate
Process insights uncovered during testing and refine prototypes and concepts based on learnings. Identify potential pivots in strategy or features.
Debrief
Review the Sprint achievements and process. Discuss what worked well and what could be improved. Capture key insights, recommendations, and next steps.
Innovation Sprint Guidelines
To maximize the impact of an Innovation Sprint, follow these proven guidelines:
Establish a Clear Focus
A narrowly defined problem or opportunity enables focused effort. Avoid vague themes that lead to scattered work and keep the goal aligned with strategic objectives.
Select a Diverse Team
Assemble 6-8 individuals from different disciplines and roles. Include varied thinking styles and experience levels as fresh perspectives drive breakthrough thinking.
Appoint a Skilled Facilitator
An experienced facilitator manages logistics, guides the exercises, enforces the process, and builds team cohesion. Choose someone well-versed in design thinking.
Create a Conducive Environment
Secure a space suitable for breakouts, brainstorming, and building. Provide ample wall space for displaying ideas and stock materials for prototyping.
Follow the Process
Maintain Sprint rhythms like stand-up meetings and timed activities. Stick to the process even when uncomfortable as creativity is challenged and flourishes under constraints.
Defer Judgment
Creativity requires psychological safety. So avoid criticizing ideas prematurely during ideation. Build on others’ ideas and evaluate later using defined criteria.
Focus on Quick Wins
Pursue simple ideas offering fast feedback over complex solutions. Simple prototypes and minimum viable products provide early customer learning.
Accommodate Flexibility
While maintaining structure, leave room to adapt based on learnings and team dynamics, and keep only what drives progress.
Conclusion
One of the goals of Agile development is faster time to market for products and services. Agile Innovation Sprints are a great way to make this happen.
It’s important to know situations where Innovation Sprints could be useful, and how to use them effectively to test and evolve ideas rapidly.
If you’re considering using them, then you can’t go wrong by following the guidelines in this article.
FAQs
How Long is an Innovation Sprint?
An ideal Innovation Sprint lasts from two to five days.