The Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE) plays a critical role in enabling organizations to achieve business agility. As part of the guiding coalition, the LACE drives the adoption of Lean-Agile principles and the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe).
This article explores the purpose, structure, and activities of an effective LACE. We’ll discuss the characteristics needed in LACE members as well as common organizational models.
Whether you’re launching a new LACE or looking to mature an existing one, this article provides actionable guidance on choosing the right implementation strategies, ensuring proper training, and sustaining the LACE.
What is Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE)?
A Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE) is a small, dedicated Agile team focused on driving your organization’s transformation to Lean-Agile.
The LACE serves as the hub of the guiding coalition, providing the training, processes, tools, and governance needed to achieve business agility.
The primary purpose of the LACE is to facilitate the adoption of Lean-Agile principles and the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe). It helps build Lean-Agile capabilities across the organization by coaching teams, launching ARTs, and supporting leadership.
The LACE manages the transformation backlog, which outlines the incremental changes needed to reach your business agility goals. It also fosters a culture of learning through training and communities of practice.

Lean-Agile Principles and Practices
The LACE helps instill key Lean-Agile principles and practices across the organization. This establishes a foundation for achieving business agility.
Some important Lean principles the LACE promotes include:
- Focus on Customer Value: Build solutions based on customer needs. Deliver value early and often.
- Whole System Optimization: Optimize the end-to-end value stream, not individual parts.
- Embrace Change: Accept change as normal and leverage it as a competitive advantage.
- Decentralize Decision-making: Empower teams to make decisions to optimize flow.
- Lean Thinking: Eliminate waste, optimize flow, and make processes and tools Lean.
The LACE also facilitates the adoption of core Agile practices including:
- Iterative Development: Deliver solutions in small batches via iterations.
- Cross-functional Teams: Build skilled, empowered teams with all the expertise to deliver value.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously identify and implement improvements via retrospectives.
- Customer Collaboration: Engage customers throughout to ensure value is delivered.
- Working Software: Focus on producing working solutions early and often.
With the LACE’s guidance, these practices become ingrained into everyday work. The LACE models these behaviors through its own operations and coaches teams on applying them. This creates an Agile culture focused on delivering maximum value.

Characteristics of a Lean-Agile Center of Excellence
An effective LACE is staffed with respected change agents who exhibit key characteristics:
• Respected by peers: Individuals who influence others and drive new behaviors despite their title.
• Motivated to help others: Passionate about helping teams/leaders adopt Lean-Agile. Focused on enabling success over personal glory.
• Pragmatic optimists: Able to identify areas for improvement in a positive, solutions-focused way. Not easily discouraged.
• Lean-Agile mindset: Embrace iteration, feedback, and continuous improvement. Comfortable with uncertainty and change.
• Strong communication skills: Can tailor messages for different audiences and communicate a compelling vision.
• Influential leadership: Lead by example. Excel at forming relationships, understanding motivations, and navigating influence.
• Expertise in change management: Skilled in coaching leaders/teams through transformation. Understand organizational change models.
• Lifelong learners: Continuously expand their Lean-Agile knowledge. Connect with communities to discover better ways of working.
With these attributes, LACE members can serve as credible coaches to teams and leaders. They become a guiding coalition that others trust to show the way towards SAFe adoption.
Roles within a Lean-Agile Center of Excellence
The roles within LACE can vary depending on the specific needs of the organization, but they typically include the following:
- LACE Lead or Director: This person leads the LACE team and is ultimately responsible for the successful adoption of Lean-Agile practices within the organization. They often work closely with senior leadership to align the organization’s strategy with its Lean-Agile transformation.
- Agile Coaches: Agile coaches guide teams through the process of adopting Agile practices. They provide training, mentorship, and support to teams as they navigate their Agile transformation. They also help to resolve any issues or obstacles that teams might encounter along the way.
- Lean-Agile Trainers: These individuals are responsible for training all members of the organization in Lean-Agile principles and practices. This might include conducting workshops, seminars, and other training activities.
- Change Agents/Change Management Specialists: These individuals are responsible for managing the organizational changes associated with the Lean-Agile transformation. They work to ensure that the changes are implemented smoothly and that they are well-received by all members of the organization.
- Data Analysts/Measurement Specialists: These individuals gather and analyze data related to the organization’s Lean-Agile transformation. They help to measure the impact of the transformation and use this information to drive continuous improvement.
- Lean-Agile Champions/Stakeholders: These are individuals from various parts of the organization who are committed to the Lean-Agile transformation. They help to promote Lean-Agile practices within their own departments or teams and serve as a bridge between the LACE and the rest of the organization.
It’s worth noting that the specific roles and their responsibilities can vary widely depending on the organization’s size, industry, and specific needs. However, the primary goal of all these roles is to facilitate the successful adoption of Lean-Agile practices throughout the organization.
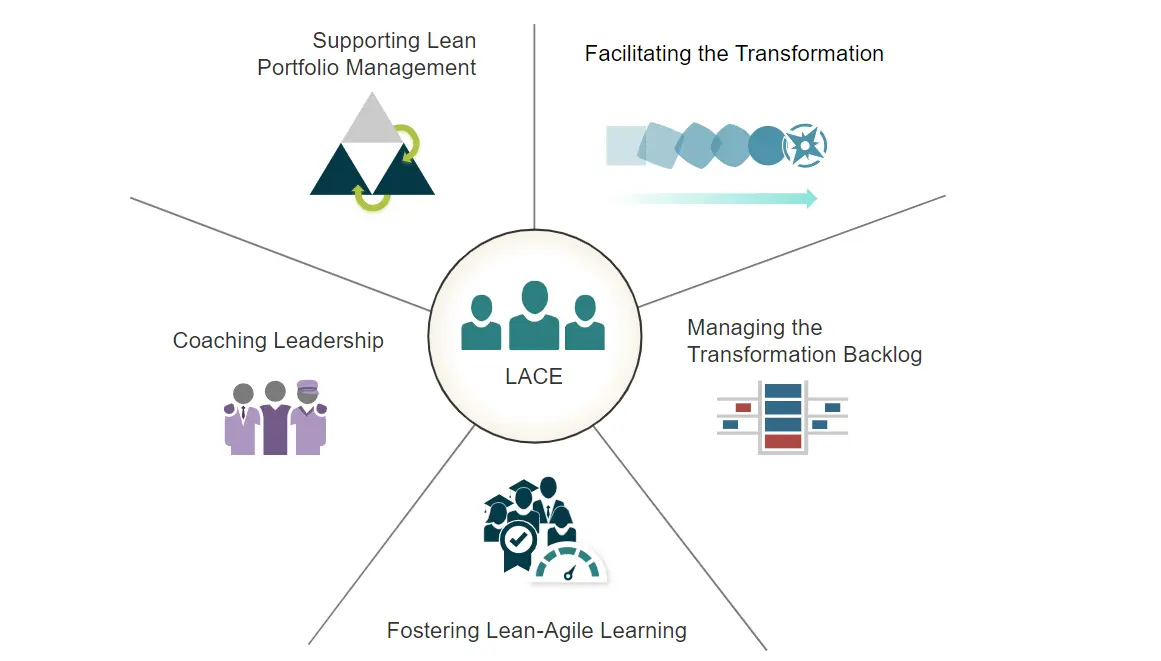
What are the Responsibilities of a Lean-Agile Center of Excellence?
The LACE has a multifaceted role in enabling organizational agility. Its core responsibilities can be grouped into five key areas:
1. Facilitating the Transformation
The LACE facilitates the adoption of Lean-Agile practices across the organization. This includes:
- Developing a clear mission statement and transformation vision
- Modeling Lean-Agile behaviors as an Agile team
- Managing communications on the transformation strategy and progress
2. Managing the Transformation Backlog
The LACE maintains a prioritized backlog of incremental changes required to reach business agility goals. This involves:
- Establishing a baseline through assessments
- Identifying measurable transformation objectives and key results (OKRs)
- Validating value and collecting feedback to continuously improve
3. Fostering Lean-Agile Learning
The LACE creates customized training programs and promotes a culture of learning, including:
- Developing role-based curriculum and learning plans
- Measuring training effectiveness through competency growth metrics
- Facilitating communities of practice
4. Coaching Leadership
The LACE coaches leaders on adopting Lean-Agile mindsets and practices via:
- Leadership workshops
- Integrating Agile coaching into existing programs
- Providing guidance on setting objectives and key results (OKRs)
5. Supporting Lean Portfolio Management
The LACE supports governance and funding decisions by:
- Facilitating LPM events
- Providing insights from the value stream
- Collaborating with the Value Management Office (VMO)
By focusing on these key responsibilities, the LACE can enable sustainable transformational change across the organization.
Lean-Agile Center of Excellence Organizational Models
Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE) organizational models can vary depending on the size, structure, and needs of an organization.
Here are three common organizational models for a LACE:
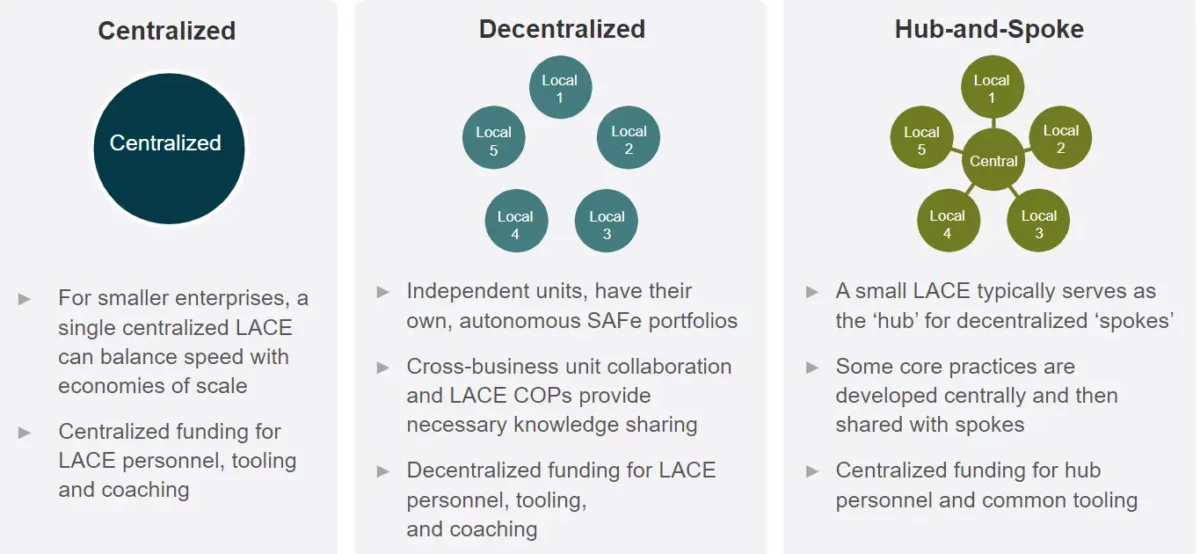
1. Centralized Model
In a centralized model, the LACE operates as a single, unified team within the organization, typically reporting to a high-level executive or C-suite leader.
This model is best suited for organizations with a strong central leadership structure and a relatively small number of teams or business units.
Advantages of the Centralized Model
- Clear communication and alignment with organizational strategy
- Consistent application of Lean-Agile practices across the organization
- Efficient resource allocation and decision-making
Disadvantages of the Centralized Model
- Potential for limited visibility into the specific needs and challenges of individual teams
- May not be as adaptable to the unique requirements of different business units
2. Decentralized Model
In a decentralized model, the LACE is organized into multiple, smaller LACE teams that are distributed across different divisions, departments, or geographic locations.
Each LACE team operates independently but is coordinated through regular communication and collaboration to ensure consistency in Lean-Agile practices and alignment with the overall organizational strategy.
Advantages of the Decentralized Model
- Greater adaptability and responsiveness to the unique needs of individual teams or business units
- Increased visibility into the challenges and opportunities at the local level
- Encourages ownership and autonomy among teams
Disadvantages of the Decentralized Model
- Potential for inconsistent application of Lean-Agile practices across the organization
- Requires strong coordination and communication mechanisms to ensure alignment
3. Hub-and-Spoke (Hybrid) Model
The hybrid hub-and-spoke model combines elements of both centralized and decentralized models. A central LACE team provides overall strategy, guidance, and support, while smaller, localized LACE teams focus on the specific needs of their respective business units or geographic locations.
This model balances the advantages of both centralized and decentralized models, allowing for consistency and alignment across the organization while still providing adaptability and responsiveness at the local level.
Advantages of the Hub-and-Spoke Model
- Consistent application of Lean-Agile practices across the organization
- Adaptability to the unique requirements of different teams and business units
- Increased visibility into local challenges and opportunities
Disadvantages of the Hub-and-Spoke Model
- Requires strong coordination and communication mechanisms to ensure alignment
- Potentially more complex and resource-intensive than other models
When choosing an organizational model for a LACE, it’s important for organizations to consider their specific needs, culture, and structure.
Factors such as size, geographic distribution, and internal leadership dynamics can all influence which model is most effective in driving a successful Lean-Agile transformation.

LACE Implementation Strategy
When establishing a new LACE, follow these steps:
Secure Executive Buy-In
- Present the LACE value proposition to executives
- Ensure their commitment as LACE Business Owners and transformation sponsors
Identify Initial Members
- Select respected change agents exhibiting key LACE characteristics
- Include cross-functional roles like coaching, training, and change management
Launch as an Agile Team
• Establish LACE rituals like retrospectives and backlog grooming
• Start modeling Lean-Agile behaviors even before formal training
Define the Mission and Vision
• Create a compelling LACE mission statement and transformation vision
• Communicate consistently to set expectations
Develop the Backlog
- Perform assessments to baseline your starting point
- Identify measurable OKRs for the LACE and overall transformation
Provide Training
• Complete Lean-Agile and SAFe training as a team
• Become certified SAFe Program Consultants (SPCs)
Publicize and Promote
• Market the LACE and its value through presentations, newsletters, etc.
• Highlight quick wins to build credibility
With the right strategy, your LACE can successfully guide the organization’s Agile transformation

Training and Development within LACE
Training is a critical enabler for developing Lean-Agile capabilities within the LACE and across the organization.
LACE Team Training
The LACE team needs foundational training to guide others:
- Attend SAFe courses together to establish shared understanding
- Become SPC certified to gain credibility as trainers
- Learn facilitation skills to deliver impactful workshops
- Pursue advanced certifications to expand expertise
Organization-Wide Training
The LACE facilitates training programs organization-wide:
- Assess role-based competencies to identify learning needs
- Create customized learning paths to incrementally build skills
- Offer SAFe and other Lean-Agile courses tailored to different teams
- Provide supplemental training on methods like Design Thinking
Communities of Practice
The LACE enables continuous learning via communities of practice (CoPs):
- Establishing CoPs for various roles to share experiences
- Hosting workshops and events for practitioners to connect
- Capturing and distributing learnings across the organization
Measuring Effectiveness
The LACE evaluates training and CoPs through:
- Gathering participant feedback
- Tracking metrics on hours and certifications
- Correlating training to outcomes like team velocity
Scaling the Lean-Agile Center of Excellence
As organizations grow and evolve, there may be a need to scale the LACE to support more teams and larger initiatives. Strategies for scaling a LACE include:
- Expanding the LACE team by adding more Agile coaches and Scrum Masters to support additional teams.
- Developing a network of internal Lean-Agile champions who can help disseminate Lean-Agile practices across the organization.
- Adopting scaling frameworks, such as the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), to provide guidance on how to effectively scale Lean-Agile practices.
Final Thoughts
The Lean-Agile Center of Excellence plays a pivotal role in guiding your Agile transformation journey. By embracing its responsibilities for change management, training, coaching, and support, the LACE can steer you towards achieving business agility.
It provides the knowledge, tools, and leadership needed to adopt Lean-Agile principles across your teams and portfolio. With the right vision and strategy, your LACE will enable you to continuously improve, adapt to change, and deliver maximum value.